Introduction
When it comes to understanding the inner workings of a vehicle, one component that often goes overlooked is the starter motor. However, this small yet crucial device plays a vital role in getting your car up and running. In this beginner’s guide, we will explore what a starter motor is and what it does.
Who invented the starter motor?
Charles Kettering invented the electric starter in 1911 for use on the 1912 Cadillacs, integrating an electric motor, generator, and spark ignition system, vastly modernizing cars of the time.
Vincent Bendix engineered a drive system that allowed the starter gears to engage or disengage quickly and effectively, which is an important part of the starting system. The generating and ignition functions would soon be divorced from the starter and get their own dedicated systems, but ironically, many modern mild hybrids use an integrated alternator/starter system once again. The pinion gear then turns the flywheel and the engine starts. As soon as the engine fires (and you let go of the ignition key) the solenoid allows the pinion gear to retract and disengage from the flywheel, preventing damage to the starter.
What is a Starter Motor?
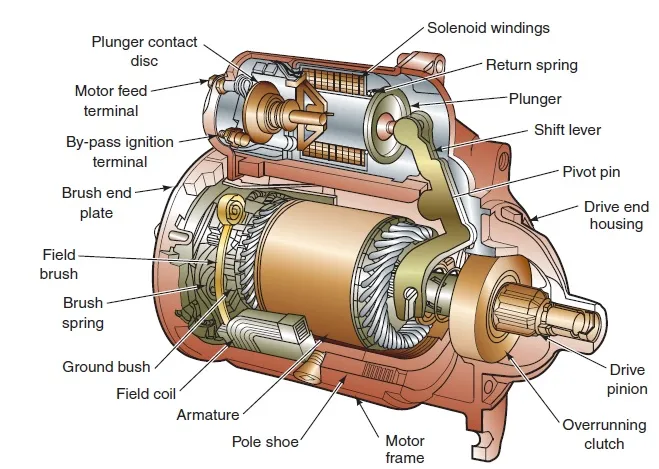
A starter motor is an electric motor that is responsible for starting the engine of a vehicle. It is typically located near the bottom of the engine, attached to the flywheel or the flexplate. The starter motor draws electrical power from the battery and converts it into mechanical energy to crank the engine and initiate the combustion process.
How Does a Starter Motor Work?
When you turn the ignition key or press the start button, an electrical signal is sent to the starter motor. This signal activates a small gear called the starter drive, which meshes with the teeth on the flywheel or flexplate. As the starter drive engages, it rotates the engine’s crankshaft, causing the pistons to move up and down in the cylinders. This, in turn, creates the necessary compression and spark for the engine to start.
Once the engine is running, the starter motor disengages from the flywheel or flexplate and stops spinning. This is achieved through a mechanism called an overrunning clutch, which allows the starter drive to freely rotate in one direction but prevents it from rotating in the opposite direction. The overrunning clutch ensures that the starter motor does not continue to spin unnecessarily once the engine is running.
Signs of a Faulty Starter Motor
Like any other mechanical component, starter motors can experience issues over time. Some common signs of a faulty starter motor include:
- The engine cranks slowly or does not crank at all
- A clicking sound when turning the ignition key
- Intermittent starting problems
- Smoke or a burning smell coming from the starter motor
- Excessive noise during engine startup
If you notice any of these signs, it is important to have your starter motor inspected and repaired by a qualified mechanic to prevent further damage to your vehicle.
What causes starter motor failure?
There are several ways a starter can fail. Here are some of the most likely issues:
- If the internal mechanical parts of the starter (the bearings for instance) start to go bad it will take more power to turn it, until eventually it doesn’t turn fast enough to start the engine.
- If the insulation on the armature winding starts to break down, the starter will not have as much torque as it once did and may not want to turn the engine over, even with a fully charged battery.
- If the starter just clicks but doesn’t turn, and the battery is fully charged, chances are the connections within the solenoid or commutator are worn or dirty and not conducting electricity as well as they should. Sometimes a starter will work fine in the morning, but not crank once it has warmed up from driving.
Maintenance and Care
While starter motors are designed to be durable, regular maintenance can help prolong their lifespan. Here are some tips to keep your starter motor in good condition:
- Ensure your battery is in good working order, as a weak or dead battery can put additional strain on the starter motor.
- Keep the starter motor and its connections clean and free from corrosion.
- Have your vehicle’s electrical system inspected regularly to identify and address any potential issues.
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommended service intervals for your vehicle.
Conclusion
A starter motor may seem like a small and insignificant component, but it plays a crucial role in getting your vehicle started. Understanding how it works and recognizing the signs of a faulty starter motor can help you address any issues before they become major problems. By taking proper care of your starter motor and maintaining your vehicle’s electrical system, you can ensure reliable and hassle-free engine starts for years to come.